5 TIPS TO IMPROVE YOUR ECOMMERCE PRODUCT CATALOG
While usability and search engine optimization are important for any site, when it comes to online retailing, merchants must consider things that are specific to eCommerce. Below are a few steps retailers can take to improve their online product catalog management strategy. These best practices will foster better user experiences, search engine rankings, and, hopefully, sales.
1) Choose the best category structure/navigation for your online store.
Mega menus can be great for retailers with large product catalogs, but problems can arise with mega menus if merchants aren’t careful. It’s important not to overwhelm the consumer or confuse them. Plus, having categories that are too specific can prevent the consumer from discovering new products they were not necessarily looking for, but may choose to buy. Here are some tips online retailers can use to prevent problems resulting from poor categorization/navigation on their websites:
- Consider the number of items in the product assortment as well as its depth and breadth. If there aren’t many items in the catalog, a mega menu is not the way to go.
- Think about how the consumer would typically shop. Perform keyword research and consider putting some subcategories in multiple parent categories.
- Remember that consumers, as well as search engines, are more likely to understand text rather than pictures for navigation menus. The primary navigation menu in the example below from HEXBUG could use improvement, as the pictures do not make it clear what category each picture represents.

- Use bold and/or larger fonts to differentiate categories from subcategories like so:
- Make parent categories clickable to allow customers to discover new products.
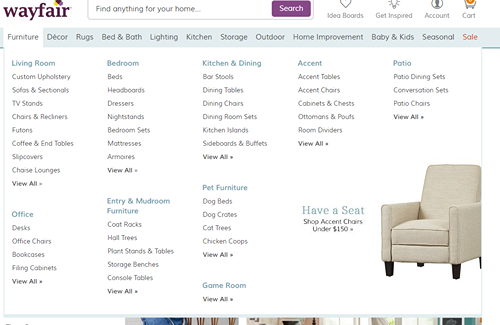
- Don’t create too many layers of categories in the primary navigation. Note that while the mega menu shown above from Wayfair has many subcategories, they are not too specific. Rather, Wayfair allows site users to narrow down by attributes like material, style, etc. on its category pages with filter options.
2) Employ cross-selling and upselling strategies.
In order to increase sales and conversion, it helps to show customers related products while they shop. This can be done both on product detail pages (PDPs) and with internal search.
- For product detail pages
- Have a “You May Also Like” type of list with related items that are similar in style or could be used along with the item the customer is currently viewing.
- For internal search
- When a customer starts typing their query in the site’s search box, show suggestions that drop down from the search bar.
- Set up synonyms, hypernyms, misspelling suggestions, and related terms to ensure customers see all products relevant to their search.
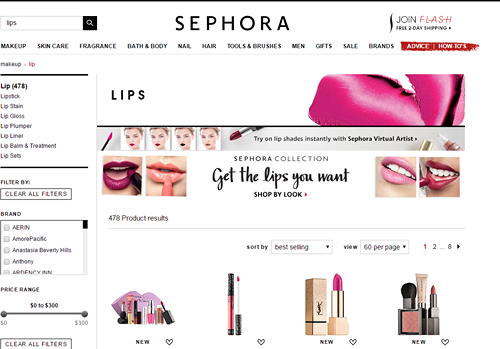
- For general searches, direct customers to category pages rather than a long list of products. That way, the customers can easily narrow down their search using relevant filter options. On Sephora’s website for example, if someone searches “lips,” they are shown the Lips category page.
3) Avoid SEO problems resulting from duplicate content.
Using the same copy for multiple product descriptions, or, say, using a description provided by a manufacturer that is on another website, counts as duplicate content, which can negatively affect SEO.
Another example of duplicate content would be when multiple paths exist to reach the same product. For example, a product may exist within multiple subcategories and thus have multiple paths. This can happen when a product can be found under a certain parent category for a specific type of clothing, as well as under a parent category for the brand. Take, for instance, the example below, which comes from ASOS.
![]()
![]()
To prevent penalties from Google as a result of duplicate content, here are a couple of actions merchants can take:
- Do not reuse old copy or place the same copy on multiple pages – be it from your own site, a manufacturer, or elsewhere.
- When multiple paths exist to reach a certain landing page, the rel=canonical tag can be used in the <head> section of the code for a webpage. The line of code would be like this (the canonical version of the page is the one you want to serve as the primary URL for the content):
<link href=“https://www.example.com/canonical-version-of-page/" rel=“canonical” />
4) Prune to help SEO.
Pruning, when talking about websites, is the practice of removing or improving pages on a site that add little value and can damage search engine rankings. It does not necessarily mean deleting pages altogether. Sometimes a retailer may temporarily deactivate an out-of-stock product and remove it from the index. They often do this if the out-of-stock item will return later. Turn to Moz for more information on when and how to prune pages for an eCommerce site.
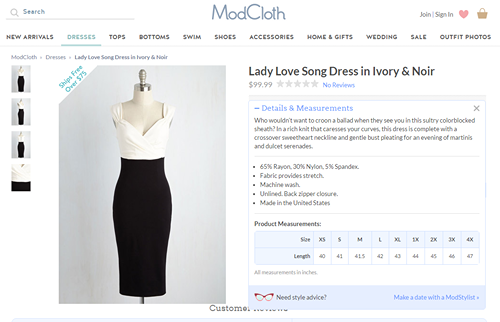
5) Optimize product descriptions.
Good product descriptions take into account not only the consumer, but also how to optimize for search engines. Here’s how to do both:
- Write a short, engaging paragraph about the item that matches the brand personality. Make sure the paragraph includes good keywords for SEO.
- Include bullet points below the paragraph with more specific information such as what the item is made of, where it’s from, etc. Do not summarize what is in the paragraph into bullet points. Here’s an example from ModCloth of a good product description: